Organizations need robust frameworks to understand the external factors that can impact their operations, strategy, and long-term success. PESTLE analysis stands as one of the most valuable and widely used strategic planning tools, helping businesses navigate the complex web of external influences that shape their operating environment.
What is PESTLE Analysis?
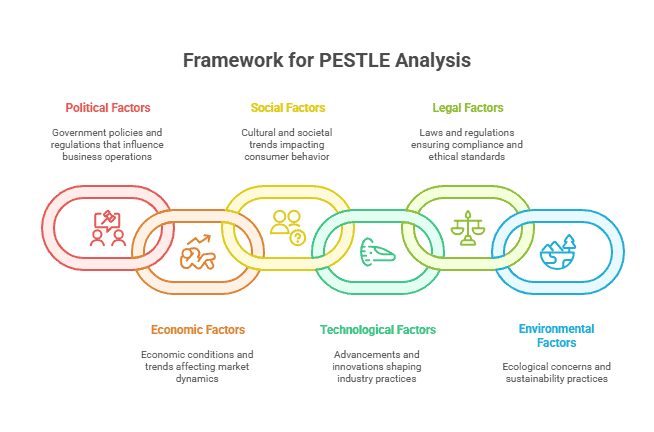
PESTLE analysis is a strategic framework used to evaluate the external macro-environmental factors that can influence an organization’s performance and decision-making. The acronym PESTLE stands for Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors. This comprehensive analytical tool enables businesses to identify opportunities and threats in their external environment, facilitating more informed strategic planning and risk management.
Originally developed as PEST analysis in the 1960s by Francis Aguilar at Harvard Business School, the framework has evolved. The addition of Legal and Environmental factors transformed PEST into PESTLE, reflecting the growing importance of regulatory compliance and sustainability in modern business operations.
The Six Components of PESTLE Analysis
1. Political Factors
Political factors encompass government policies, political stability, and regulatory changes that can significantly impact business operations. These factors influence the business environment through various mechanisms and can create both opportunities and challenges for organizations.
Key political considerations include:
- Government stability and policy changes
- Tax policies and trade regulations
- Political risk in different markets
- Government intervention in specific industries
- International trade agreements and tariffs
- Lobbying groups and political pressure
- Corruption levels and transparency initiatives
Political factors can dramatically affect market conditions. For instance, changes in healthcare policies can impact pharmaceutical companies, while shifts in environmental regulations can affect manufacturing industries. Companies operating internationally must navigate diverse political landscapes, making political analysis essential for effective global expansion strategies.
2. Economic Factors
Economic factors relate to the broader economic environment and how economic conditions affect business performance. These factors influence consumer spending power, business costs, and overall market demand.
Critical economic elements include:
- Economic growth rates and GDP trends
- Inflation rates and currency exchange rates
- Interest rates and monetary policy
- Unemployment levels and labor market conditions
- Consumer confidence and spending patterns
- Credit availability and financial market conditions
- Economic cycles and recession risks
Understanding economic factors helps businesses forecast demand, plan pricing strategies, and make investment decisions. During economic downturns, companies might focus on cost-cutting and efficiency improvements, while economic growth periods might present expansion opportunities.
3. Social Factors
Social factors examine the cultural, demographic, and social trends that influence consumer behavior and market demand. These factors help businesses understand their target markets and adapt their offerings accordingly.
Important social considerations include:
- Demographic changes and population trends
- Cultural values and lifestyle changes
- Education levels and skill availability
- Health consciousness and wellness trends
- Income distribution and social mobility
- Consumer attitudes and preferences
- Social media influence and digital behavior
Social factors are particularly important for consumer-facing businesses. For example, increasing health consciousness has created opportunities in the organic food and fitness industries, while demographic shifts like aging populations have implications for healthcare and financial services.
4. Technological Factors
Technological factors assess how technological changes and innovations can impact business operations, create new opportunities, or disrupt existing business models. In our digital age, technological factors often drive the most significant changes in business environments.
Key technological aspects include:
- Rate of technological advancement and innovation
- Automation and artificial intelligence developments
- Digital transformation trends
- Research and development investments
- Technology infrastructure and accessibility
- Cybersecurity threats and data protection
- Emerging technologies and their potential impact
Technology can be both an enabler and a disruptor. Companies that successfully leverage technological advances can gain competitive advantages, while those that fail to adapt may find themselves obsolete. The rise of e-commerce, mobile technology, and artificial intelligence exemplifies how technological factors can reshape entire industries.
5. Legal Factors
Legal factors encompass the laws, regulations, and legal requirements that businesses must comply with in their operating jurisdictions. These factors often overlap with political factors but focus specifically on the legal framework governing business operations.
Essential legal considerations include:
- Employment laws and labor regulations
- Health and safety requirements
- Consumer protection laws
- Antitrust and competition regulations
- Intellectual property rights
- Data protection and privacy laws
- Industry-specific regulations and compliance requirements
Legal factors can significantly impact operational costs and business practices. For instance, GDPR implementation affected how companies worldwide handle customer data, while changes in employment laws can impact hiring practices and operational expenses.
6. Environmental Factors
Environmental factors examine how environmental and sustainability concerns affect business operations and strategy. With growing awareness of climate change and environmental responsibility, these factors have become increasingly important for business planning.
Critical environmental elements include:
- Climate change and weather patterns
- Environmental regulations and sustainability requirements
- Carbon footprint and emissions standards
- Waste management and recycling requirements
- Natural resource availability and scarcity
- Consumer environmental consciousness
- Corporate social responsibility expectations
Environmental factors influence both regulatory compliance and consumer preferences. Companies increasingly need to consider their environmental impact, implement sustainable practices, and communicate their environmental commitments to stakeholders.
How to Conduct a PESTLE Analysis
Step 1: Define Your Scope and Objectives
Before beginning the analysis, clearly define what you want to achieve and the scope of your investigation. Determine whether you’re analyzing your current market, a potential new market, a specific product line, or your entire organization. Establish the time frame for your analysis and identify key stakeholders who should be involved in the process.
Step 2: Gather Information and Data
Collect relevant information for each PESTLE factor from reliable sources. This may include government reports, industry publications, market research, news articles, and expert opinions. Ensure your data is current and relevant to your specific context and objectives.
Step 3: Analyze Each Factor
Systematically examine each PESTLE component and identify the specific factors that could impact your business. Consider both positive and negative influences, and assess the likelihood and potential impact of each factor. Use brainstorming sessions with diverse team members to ensure comprehensive coverage.
Step 4: Assess Impact and Prioritize
Evaluate the potential impact of each identified factor on your business objectives. Consider both the probability of occurrence and the magnitude of potential impact. Prioritize factors based on their significance to your organization’s success.
Step 5: Develop Strategic Responses
Based on your analysis, develop strategic responses to address the most significant factors. This might involve capitalizing on opportunities, mitigating risks, or adapting business strategies to changing conditions.
Step 6: Monitor and Update
PESTLE analysis is not a one-time exercise. Regularly update your analysis to reflect changing conditions and new developments. Establish monitoring systems to track key indicators and trigger strategy reviews when significant changes occur.
Benefits of PESTLE Analysis
PESTLE analysis offers numerous advantages for strategic business planning and decision-making. Understanding these benefits helps organizations maximize the value they derive from this analytical framework.
- Strategic Planning Enhancement: PESTLE analysis provides a structured approach to environmental scanning, ensuring that strategic planning considers all relevant external factors. This comprehensive perspective helps organizations develop more robust and adaptable strategies that account for various external influences.
- Risk Identification and Mitigation: By systematically examining external factors, organizations can identify potential risks before they materialize. This proactive approach enables better risk management and contingency planning, reducing the likelihood of strategic surprises.
- Opportunity Recognition: PESTLE analysis helps organizations identify emerging opportunities in their external environment. Whether these opportunities arise from regulatory changes, technological advances, or social trends, early recognition provides competitive advantages.
- Market Understanding: The framework enhances understanding of market dynamics and customer needs, particularly through social and economic factor analysis. This improved market insight supports better marketing strategies and product development decisions.
- Investment and Expansion Decisions: PESTLE analysis is particularly valuable when evaluating new markets, investment opportunities, or expansion strategies. It provides a systematic way to assess the attractiveness and viability of different options.
Limitations and Considerations
While PESTLE analysis is a valuable tool, it’s important to understand its limitations and use it appropriately within your strategic planning process.
- Complexity and Interconnectedness: External factors often interact in complex ways that can be difficult to predict or model. A change in one area might trigger unexpected consequences in others, making it challenging to fully anticipate all implications.
- Data Quality and Availability: The effectiveness of PESTLE analysis depends heavily on the quality and availability of relevant data. In some markets or for certain factors, reliable information may be scarce or outdated.
- Subjectivity in Interpretation: Different analysts may interpret the same information differently, leading to varying conclusions about factor importance and impact. This subjectivity can be both a strength and a weakness of the framework.
- Dynamic Nature of External Environment: The business environment changes rapidly, and factors identified in a PESTLE analysis may quickly become outdated. Regular updates are essential but can be resource-intensive.
- Action Orientation: PESTLE analysis is primarily a diagnostic tool and doesn’t automatically generate specific action plans. Organizations need to translate insights into concrete strategies and implementation plans.
Best Practices for Effective PESTLE Analysis
To maximize the value of PESTLE analysis, consider these best practices that enhance the quality and usefulness of your analysis.
- Involve Diverse Perspectives: Include team members from different departments, backgrounds, and levels of experience in your PESTLE analysis. Diverse perspectives help identify factors that might be overlooked and provide varied interpretations of their significance.
- Use Multiple Information Sources: Rely on various credible sources for your information gathering. This might include government publications, industry reports, academic research, expert interviews, and reputable news sources. Cross-reference information to ensure accuracy and completeness.
- Focus on Relevance: While comprehensiveness is important, focus primarily on factors that are most relevant to your organization and objectives. Not all external factors will have equal impact on your business, so prioritize accordingly.
- Consider Interconnections: Examine how different PESTLE factors might interact with each other. For example, political changes might trigger economic consequences, or technological advances might create new legal requirements.
- Quantify When Possible: Where feasible, try to quantify the potential impact of different factors. This might involve scenario planning, sensitivity analysis, or other quantitative techniques that help prioritize factors and inform decision-making.
- Regular Updates: Establish a schedule for reviewing and updating your PESTLE analysis. The frequency will depend on the volatility of your industry and external environment, but quarterly or semi-annual reviews are common.
PESTLE Analysis in Different Contexts
PESTLE analysis can be applied in various business contexts, each with specific considerations and applications.
- Market Entry Strategies: When considering entry into new geographic or product markets, PESTLE analysis helps evaluate the attractiveness and feasibility of different options. It’s particularly valuable for international expansion, where political, legal, and cultural factors can vary significantly.
- Merger and Acquisition Analysis: PESTLE analysis can inform M&A decisions by identifying external factors that might affect the success of potential combinations. This includes regulatory approval processes, market conditions, and integration challenges.
- Industry Analysis: Use PESTLE analysis to understand industry dynamics and competitive landscapes. This application helps identify industry trends, growth drivers, and potential disruptions that could affect all industry participants.
- Product Development: PESTLE analysis can inform product development strategies by identifying market needs, regulatory requirements, and technological opportunities that should influence product design and positioning.
- Crisis Management: During crisis situations, PESTLE analysis helps organizations understand the full scope of external factors affecting their operations and develop comprehensive response strategies.
Conclusion
PESTLE analysis remains one of the most valuable frameworks for understanding the external business environment and informing strategic decision-making. Its systematic approach to examining political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors provides organizations with comprehensive insights into the forces shaping their operating environment.
The key to successful PESTLE analysis lies in its proper implementation and integration into broader strategic planning processes. Organizations that use PESTLE analysis effectively combine it with other analytical tools, involve diverse stakeholders in the process, and translate insights into actionable strategies.
As business environments continue to evolve at an accelerating pace, the importance of systematic environmental scanning tools like PESTLE analysis will only increase. Organizations that master this analytical framework will be better positioned to anticipate changes, identify opportunities, manage risks, and achieve sustainable competitive advantage in their markets.
Remember that PESTLE analysis is not an end in itself but rather a means to better strategic decision-making. The true value of the framework emerges when organizations use its insights to adapt their strategies, improve their operations, and create value for their stakeholders in an ever-changing business landscape.